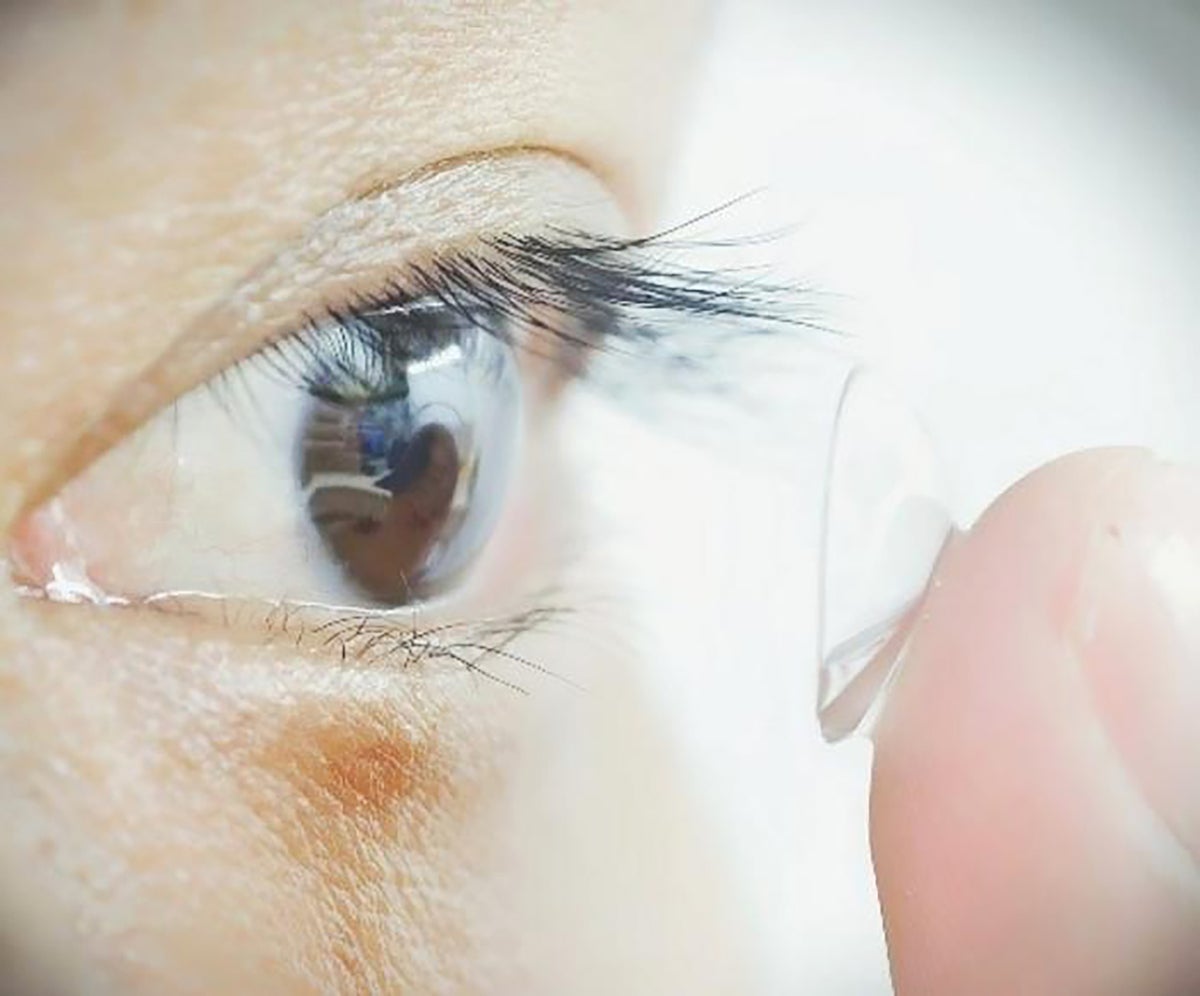
New Contacts Let You See Infrared Light—Even with Your Eyes Closed
Straight out of science fiction, these contact lenses convert infrared light into visible light that humans can see
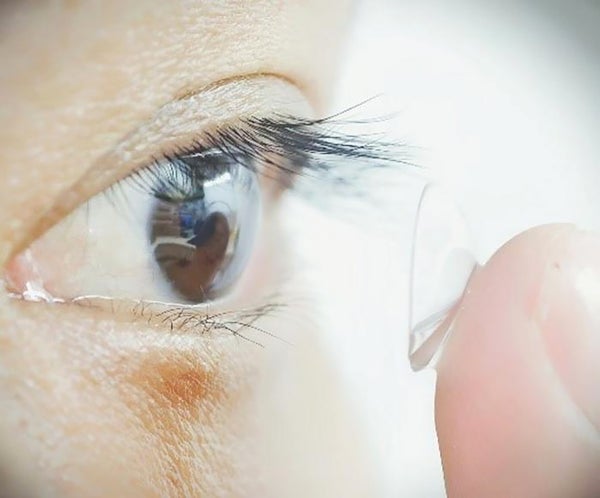
People who tested a new type of designer contact lens could see flashing infrared signals from a light source.
Humans have a new way of seeing infrared light, without the need for clunky night-vision goggles. Researchers have made the first contact lenses to convey infrared vision — and the devices work even when people have their eyes closed.
The team behind the invention, led by scientists at the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) in Hefei, gave the lenses their power by infusing them with nanoparticles that convert near-infrared light in the 800–1,600-nanometre range into shorter-wavelength, visible light that humans can see, in the 400–700-nanometre range. The researchers estimate that the lenses cost around US$200 per pair to make.
The technology, which was detailed in Cell on 22 May, “is incredibly cool, just like something out of a science-fiction movie”, says Xiaomin Li, a chemist at Fudan University in Shanghai, China. It opens up “new possibilities for understanding the world around us”, he adds.
On supporting science journalism
If you’re enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
Pros and cons
Near-infrared light sits just outside the range of wavelengths that humans can normally detect. Some animals can sense infrared light, although probably not well enough to form images.
Night-vision goggles enable humans to see infrared radiation, but they are bulky and require a power source to work. The new lenses avoid these limitations while also offering richer, multi-coloured infrared images that night-vision goggles, which operate on a monochrome green scale, typically do not.
However, the lenses do have their own shortcomings. Because the embedded nanoparticles scatter light, the images the lenses create are blurry. The team partially corrected this by putting the technology into glasses with additional lenses that redirect the light. Moreover, unlike night-vision goggles, which amplify light to detect low-level infrared signals, the lenses allow users to see only intense infrared signals, such as those emitted by light-emitting diodes (LEDs).
For these reasons, some critics don’t think the lenses will prove useful. “I cannot think of any application that would not be fundamentally simpler with infrared goggles,” says Glen Jeffery, a neuroscientist at University College London who specializes in eye health. “Evolution has avoided this for a good reason.”
Nevertheless, the authors think that their lenses can be further optimized and foresee several possible uses for the invention. For instance, wearers would be able to read anti-counterfeit marks that emit infrared wavelengths but are otherwise invisible to the human eye, says co-author Yuqian Ma, a neuroscientist at the USTC.
Li, who was not involved in the work, offers another possibility: the lenses might be worn by doctors conducting near-infrared fluorescence surgery, to directly detect and remove cancerous lesions “without relying on bulky traditional equipment”.
‘An exhilarating moment’
To create the contact lenses, the scientists built on previous research in which they gave mice infrared vision by injecting nanoparticles into the animals’ retinas. This time, they took a less invasive approach and added nanoparticles made of rare-earth metals including ytterbium and erbium to a soup of polymer building blocks to form the soft lenses, and then tested them for safety.
The main challenge, Ma says, was to pack enough nanoparticles into the lenses to convert sufficient infrared light into detectable visible light, while not otherwise altering the lenses’ optical properties, including their transparency.
Tests in mice showed that animals wearing the lenses tended to choose a dark box that was considered ‘safe’ over one lit up by infrared light, whereas mice without the lenses showed no preference for either box. Humans wearing the lenses could see flickering infrared light from an LED well enough to both pick up Morse code signals and sense which direction the signals were coming from. The lenses’ performance even improved when participants closed their eyes, because near-infrared light easily penetrates the eyelids, whereas visible light, which could have interfered with image formation, does so to a lesser degree.
“Witnessing people wearing contact lenses and successfully seeing infrared flashes was undoubtedly an exhilarating moment,” Ma says.
The team now plans to find ways to cram more nanoparticles into the lenses and hopes to develop particles that can convert light with higher efficiency, to improve the technology’s sensitivity. “We have overcome the physiological limitations of human vision, as if opening a brand-new window onto the world,” Ma says.
This article is reproduced with permission and was first published on May 22, 2025.


